Overview
Optical Coating and Thin-Film Engineering is a core research and technology area dedicated to the theoretical design, fabrication, and advanced characterization of nanometres-scale thin films that precisely control the propagation and interaction of light with matter. By engineering multilayer optical structures with accurately defined thicknesses and refractive indices, optical coatings enable tailored control of reflection, transmission, absorption, phase, and polarization across ultraviolet (UV), visible, near-infrared (NIR), mid-infrared (MIR), and far-infrared spectral regions.
Using advanced thin-film deposition technologies, optical coatings are applied to a wide range of optical components, including lenses, mirrors, filters, windows, and optoelectronic devices. These coatings enhance system performance by reducing unwanted reflections, increasing optical efficiency, enabling spectral selectivity, and providing environmental and thermal protection.
Optical coatings are fundamental building blocks of modern photonic, optoelectronic, and energy-related systems. Their performance directly determines system efficiency, spectral stability, and long-term reliability. The Optical Coating & Thin-Film Engineering work area integrates optical theory, materials science, nanofabrication, and precision metrology to develop high-performance coatings for both advanced scientific research and real-world technological applications.

Optical Coating & Thin-Film Engineering
Theoretical Foundations of Optical Coatings
The design of optical coatings is based on electromagnetic wave theory and thin-film interference phenomena, where multiple reflections at interfaces between layers with different refractive indices lead to constructive or destructive interference. By controlling the optical thickness (physical thickness × refractive index) of each layer relative to the operating wavelength, the spectral response of the coating can be precisely engineered.
Key theoretical principles include:
- Fresnel equations governing reflection and transmission at interfaces
- Transfer matrix methods for modelling multilayer optical stacks
- Dispersion engineering through wavelength-dependent refractive indices
- Phase control and optical admittance matching for broadband performance
- Polarization-dependent behaviour in anisotropic and multilayer systems
Advanced coating designs may incorporate chirped structures, gradient-index layers, and nanocomposite materials to achieve broadband, angularly robust, or spectrally selective optical responses.
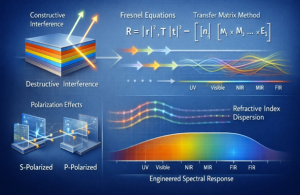
Theoretical Foundations of Optical Coatings
Thin-Film Materials and Deposition Technologies
This work area focuses on the deposition and integration of a wide range of dielectric, metallic, semiconductor, and hybrid thin-film materials, selected according to optical performance, thermal stability, and environmental durability requirements.
Key fabrication approaches include:
- Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) techniques such as sputtering and thermal evaporation
- Multilayer dielectric stack fabrication with nanometres-level thickness control
- Optical coatings on glass, crystalline substrates, semiconductor wafers, optical Fiber. Etc
- Low-loss, high-uniformity coatings for precision optical systems
Material systems commonly studied include high- and low-refractive-index dielectrics, transparent conductive oxides, infrared-compatible materials, and protective overcoats for harsh environments.
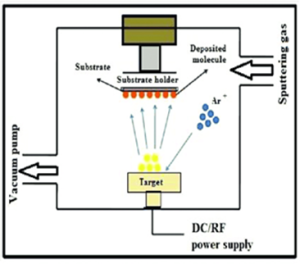
Sputtering System
Optical Coating Design Using Essential Macleod
Essential Macleod is a powerful and industry-standard software platform for the design, simulation, and optimization of optical thin-film coatings. It enables rigorous modelling of multilayer structures deposited on glass substrates by solving the electromagnetic response of stratified media using transfer-matrix methods.
In optical coating design workflows, Essential Macleod is used to:
- Define substrate materials with accurate dispersion models
- Build multilayer coating stacks with user-defined materials and thicknesses
- Simulate spectral performance (reflection, transmission, absorption)
- Analyse angular and polarization dependence
- Optimize designs using target functions and merit optimization algorithms
The software allows designers to precisely tailor coating performance for specific wavelength ranges and incidence conditions while accounting for real material behaviour.
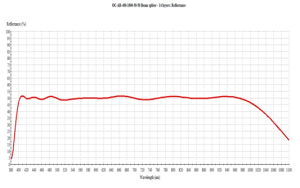
Beam splitter 50%R, 50%T for visible band
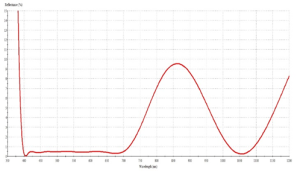
Dual Band AR coating (420–700 nm) & (1064 nm)
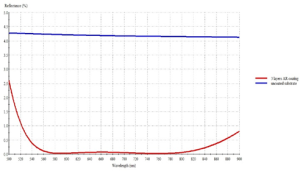
Anti-reflection coating design optimized for the 560–825 nm wavelength range
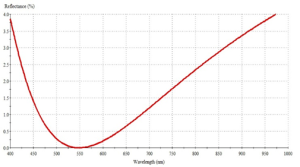
Single layer (single-point AR coating) on S-NPH2
Application Areas
Optical Coating & Thin-Film Engineering supports a broad spectrum of high-impact applications:
- Optics & Photonics: lenses, mirrors, lasers, optical filters
- Antireflection coatings for lenses, windows, and photovoltaic cover glass
- High-transmission optical windows for UV, visible, and infrared systems
- Beam splitters and neutral density filters
- Laser optics and protective windows
- Display, imaging, and sensing systems
- Telecommunications: optical fibers and wavelength-division components
- Medical Technology: imaging, diagnostics, and laser surgery
- Military & Defence: night-vision systems, thermal imaging, stealth, and laser optics
- Aerospace & Space: satellite optics, space telescopes, radiation- and UV-resistant coatings
- Sensors & Consumer Devices: detectors, smartphones, and wearables
- Electronics & Semiconductors: integrated circuits, displays, MEMS
- Energy Systems: solar cells and thermal absorbers
- Automotive & Architecture: LIDAR, HUDs, smart and low-emissivity windows
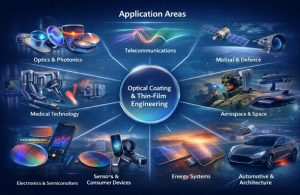
Overview of key application areas enabled by optical coating and thin-film engineering across multiple industries
Research Vision and Impact
The Optical Coating & Thin-Film Engineering work area serves as a multidisciplinary platform connecting optics, nanotechnology, materials science, and device engineering. Research efforts aim to push the limits of optical performance through innovative coating architectures, new material systems, and precision fabrication techniques.
By combining rigorous optical theory with state-of-the-art experimental capabilities, this department contributes to next-generation photonic technologies for scientific research, industrial applications, and emerging optoelectronic systems.